Analysis of Asian Stock Market Performance on February 21st
Introduction
The Asian stock market is a crucial player in the global economy, often serving as an indicator of broader economic trends. Understanding its performance on specific days, such as February 21st, requires a comprehensive analysis encompassing various factors including economic indicators, geopolitical events, and market sentiment. In this analysis, we delve into the performance of the Asian stock market on February 21st, examining key indices, notable trends, and the underlying drivers influencing market movements.
Market Overview
On February 21st, the Asian stock market witnessed mixed performance across different indices. While some markets experienced gains, others faced losses, reflecting a diverse array of regional and global influences impacting investor sentiment.
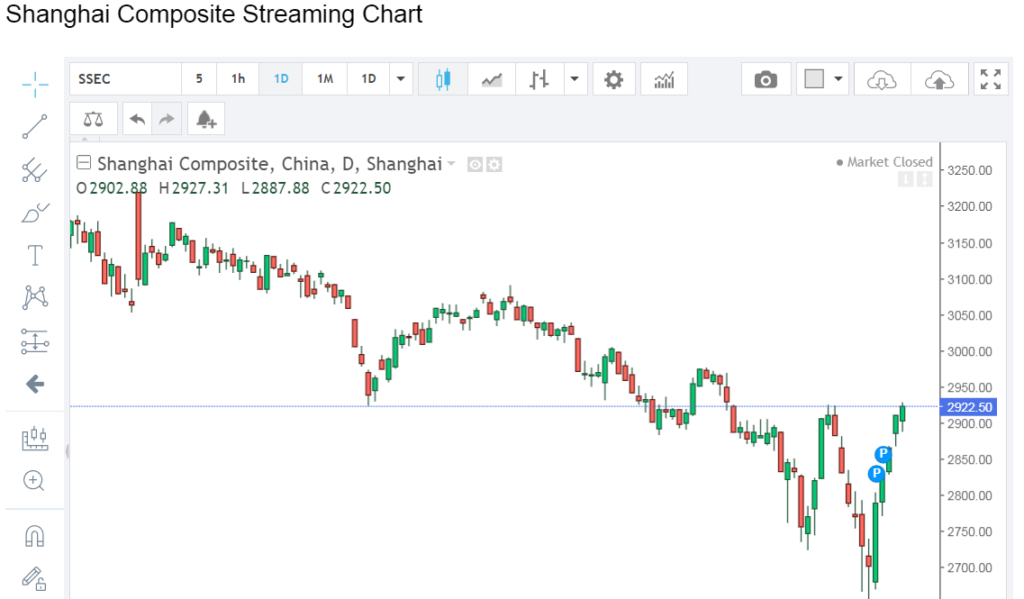
1. Shanghai Composite (China)
The Shanghai Composite Index, representing the performance of China’s stock market, showed resilience on February 21st, posting modest gains despite prevailing uncertainties. Improved investor confidence, supported by positive economic data and government stimulus measures, contributed to the index’s upward trajectory. Additionally, progress in U.S.-China trade talks provided further optimism, although concerns over geopolitical tensions and regulatory crackdowns lingered, tempering overall market sentiment.
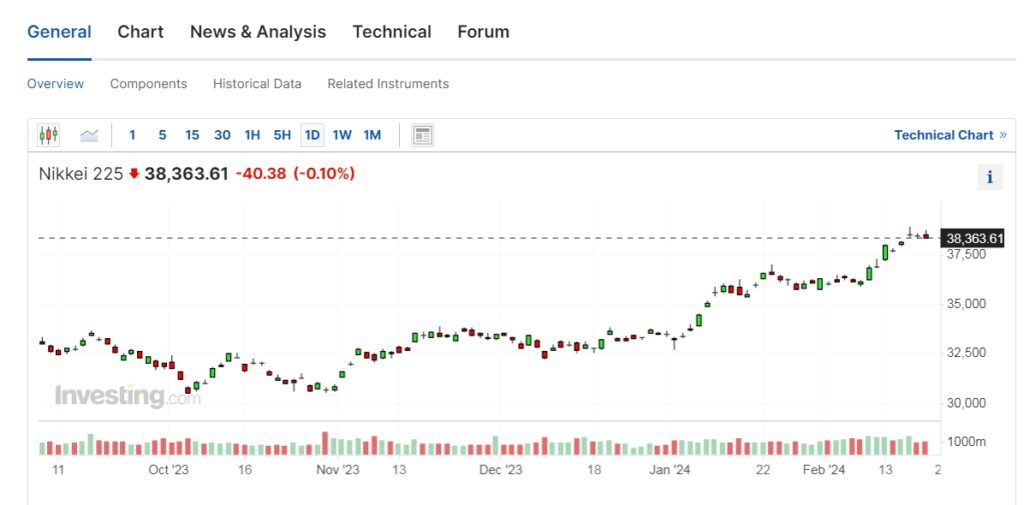
2. Nikkei 225 (Japan)
In contrast, Japan’s Nikkei 225 index struggled to maintain momentum on February 21st, closing marginally lower amid mixed signals from the domestic economy. Weighed down by disappointing corporate earnings reports and lingering concerns over the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on economic recovery, investor sentiment remained subdued. Moreover, uncertainty surrounding the Bank of Japan’s monetary policy stance added to market volatility, as investors awaited clearer signals regarding future policy direction.
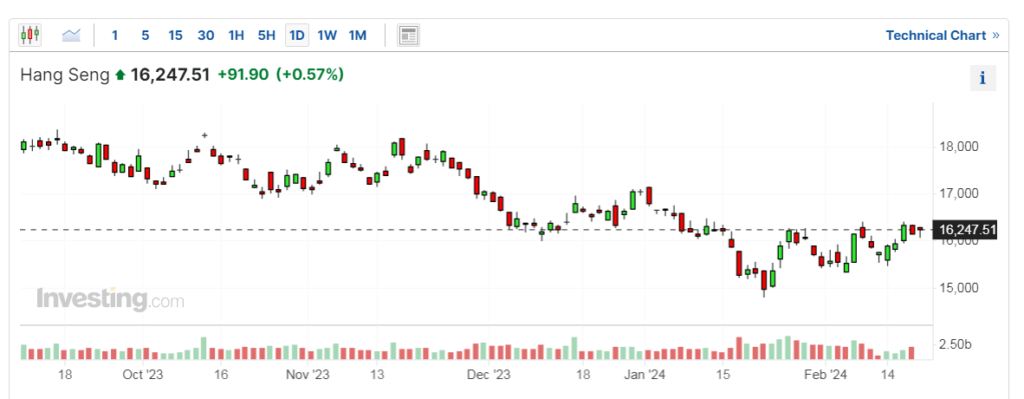
3. Hang Seng Index (Hong Kong)
The Hang Seng Index faced notable headwinds on February 21st, ending the trading day with significant losses driven by a confluence of factors. Escalating geopolitical tensions, particularly in the context of Sino-U.S. relations, weighed heavily on investor confidence, as concerns over potential sanctions and regulatory measures intensified. Furthermore, ongoing protests and social unrest in Hong Kong added to the prevailing climate of uncertainty, exacerbating market volatility and prompting investors to adopt a cautious stance.
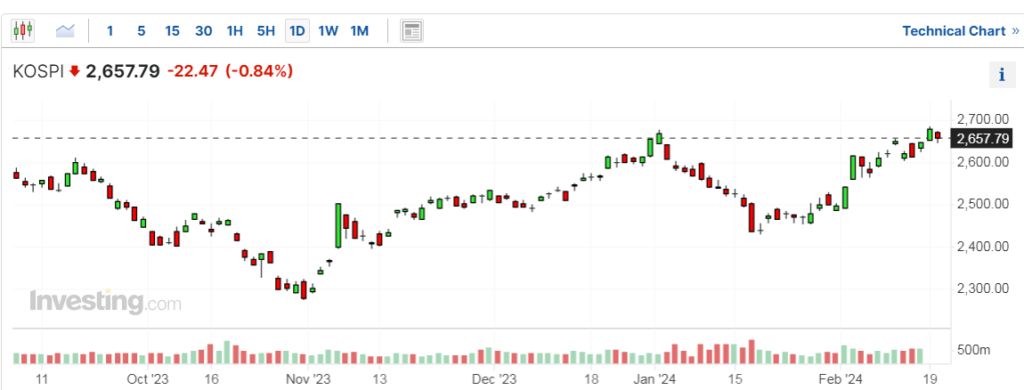
4. KOSPI (South Korea)
South Korea’s KOSPI index exhibited resilience on February 21st, bucking the broader regional trend with marginal gains supported by positive economic data and strong corporate earnings. Robust exports, particularly in the technology sector, bolstered market sentiment, while government stimulus measures aimed at fostering economic recovery provided additional support. However, lingering concerns over geopolitical tensions on the Korean peninsula tempered overall optimism, contributing to subdued trading activity.
Key Drivers and Influences
Several key drivers and influences shaped the performance of the Asian stock market on February 21st, encompassing both domestic and external factors:
1. Economic Data: The release of economic indicators, including GDP growth, inflation rates, and manufacturing PMI data, played a pivotal role in shaping investor sentiment and market movements. Positive data points, such as robust export figures or improving consumer confidence, often bolstered investor confidence and contributed to market gains.
2. Geopolitical Events: Geopolitical tensions and diplomatic developments, particularly those involving major economies such as the United States, China, and North Korea, exerted a significant impact on market sentiment. Escalating tensions, trade disputes, or geopolitical crises often led to heightened volatility and risk aversion among investors.
3. Monetary Policy: Central bank actions and monetary policy decisions, including interest rate changes, quantitative easing measures, and forward guidance, influenced investor expectations and market dynamics. Clarity and consistency in central bank communication were crucial in guiding investor sentiment and shaping market outcomes.
4. Corporate Earnings: The release of corporate earnings reports and financial performance assessments provided insights into the health and profitability of individual companies and sectors. Positive earnings surprises or strong guidance often resulted in upward stock price movements, while disappointing results could lead to sell-offs and market declines.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the performance of the Asian stock market on February 21st reflected a complex interplay of domestic and external factors, with divergent trends observed across different indices. While some markets exhibited resilience and posted gains, others faced challenges amid lingering uncertainties and geopolitical tensions. Understanding the underlying drivers and influences shaping market dynamics is crucial for investors seeking to navigate volatile conditions and make informed decisions in the ever-evolving landscape of the Asian stock market.